The software industry stands at an inflection point. Organizations managing critical systems, processing sensitive data, and competing in cloud-native environments face mounting pressure to deliver reliable, secure, and performant applications. Enter Rust – a programming language that is fundamentally reshaping how enterprises approach software development. What began as a systems programming language gaining traction in open-source projects has evolved into a strategic business imperative.
Major cloud providers, security agencies, and Fortune 500 companies are increasingly recognizing that Rust is not merely a technical preference but a catalyst for transforming business outcomes.
The Business Case for Memory Safety
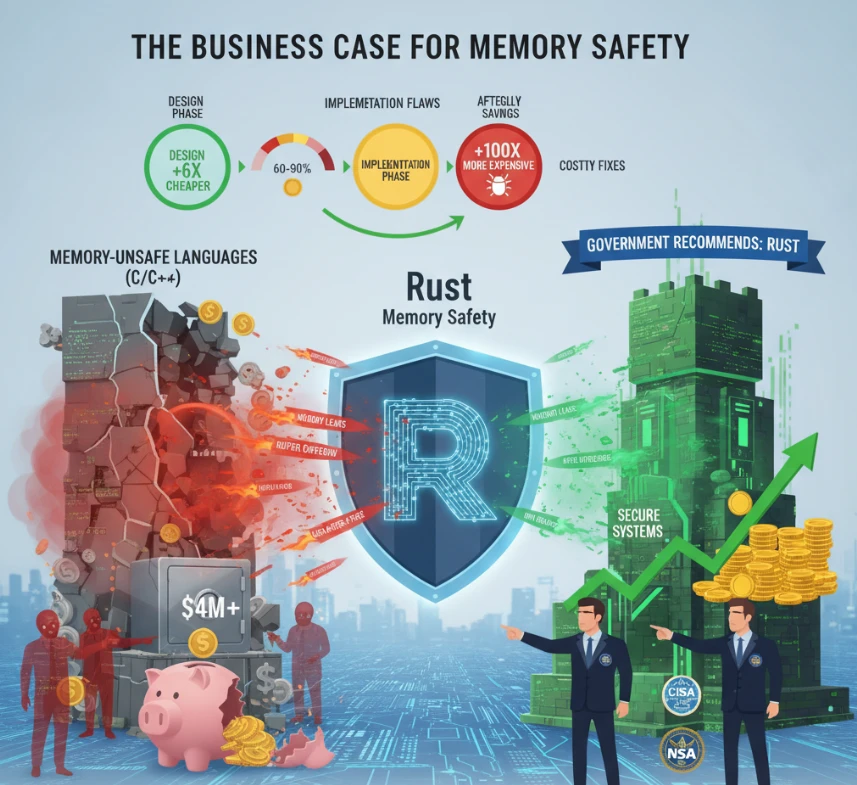
At its core, the enterprise case for Rust centers on a seemingly technical problem with profound business implications: memory safety. Memory-related vulnerabilities represent between 60 and 90 percent of all software flaws in memory-unsafe languages. These vulnerabilities carry enormous costs. The average data breach expense for enterprises now exceeds $4 million per incident, and memory safety issues frequently underpin the exploits that trigger these breaches.
Rust’s ownership model fundamentally transforms how memory is managed within applications. Unlike languages that require manual memory management or rely on garbage collection, Rust enforces memory safety rules at compile time—before code ever reaches production. This distinction is not merely theoretical.
The Economics of Early Bug Detection
The cost to fix a bug discovered during the design phase is approximately six times lower than fixing one found during implementation, and up to 100 times lower than addressing it after release. When applied to memory safety issues that Rust catches automatically, this cost differential translates into substantial savings. Organizations no longer need to allocate resources to track down memory leaks, buffer overflows, or use-after-free errors in production environments.
Government agencies have taken notice. The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the National Security Agency jointly recommended transitioning from C and C++ to memory-safe languages like Rust, citing systemic security risks that demand proactive solutions. This guidance represents a watershed moment—security agencies previously focused on managing vulnerabilities are now advocating for languages that prevent entire categories of vulnerabilities by design.
Rapid Enterprise Adoption: The Numbers Tell the Story
The business community is responding decisively. Rust adoption has surged dramatically, with adoption rates increasing from 1.05 percent in 2024 to 1.47 percent in 2025—a 40 percent relative increase in a single year. More significantly, business adoption has increased 68.75 percent, with 709,000 developers now identifying Rust as their primary language. This growth reflects not enthusiast experimentation but deliberate enterprise investment.
Major Enterprise Deployments
The roster of companies deploying Rust in production reads like a who’s-who of technology leadership. Amazon Web Services uses Rust extensively for infrastructure-level networking and systems software, recognizing it as essential for their most performance-critical services. Discord rewrote their real-time multiplayer syncing server—used by millions of users simultaneously—entirely in Rust, prioritizing both reliability and performance. Figma similarly leverages Rust for their core collaborative editing platform. These are not niche applications but mission-critical systems serving billions of users.
Google took a particularly visible step by integrating approximately 1.5 million lines of Rust code into Android 13, representing about 21 percent of all new native code across multiple critical system components including security infrastructure, wireless connectivity, and virtualization frameworks. This investment directly improves the security posture of billions of mobile devices globally.

Companies like Yalantis and other technology service providers have recognized this trend, increasingly incorporating Rust development services into their portfolios to meet growing enterprise demand for memory-safe, high-performance solutions.
Developer Productivity and Infrastructure Efficiency
While security captures headlines, the business benefits of Rust extend significantly into developer productivity and infrastructure economics. Amazon’s builder tools team achieved a remarkable 40 percent reduction in developer build times across the organization by strategically rewriting performance-critical sections in Rust, with individual components showing improvements ranging from 100 to 200 times faster execution.
Shorter build times directly translate to faster iteration cycles, enabling developers to maintain better engagement and ship features more rapidly. When developers spend less time waiting for compilation, they maintain better focus and cognitive flow, reducing context-switching costs that traditionally plague software development teams.
Infrastructure Cost Reductions
Infrastructure efficiency represents a second major economic benefit. Rust applications consume substantially less memory and computing resources than equivalent implementations in interpreted languages. Organizations migrating machine learning workloads from Python to Rust report infrastructure cost reductions of up to 50 percent—maintaining equivalent performance while halving server requirements.
For enterprises managing large-scale cloud deployments, these efficiency gains accumulate into millions of dollars in annual savings. A typical enterprise running thousands of microservices can realize significant cost reductions by strategically migrating high-throughput services to Rust, reducing both compute instance counts and memory allocations across their infrastructure.
The compounding effect of these improvements—fewer critical bugs, faster development cycles, reduced infrastructure costs—creates a compelling total cost of ownership advantage, particularly for long-lived enterprise systems where maintenance expenses often exceed initial development costs.
Security at Scale: Ecosystem Maturity
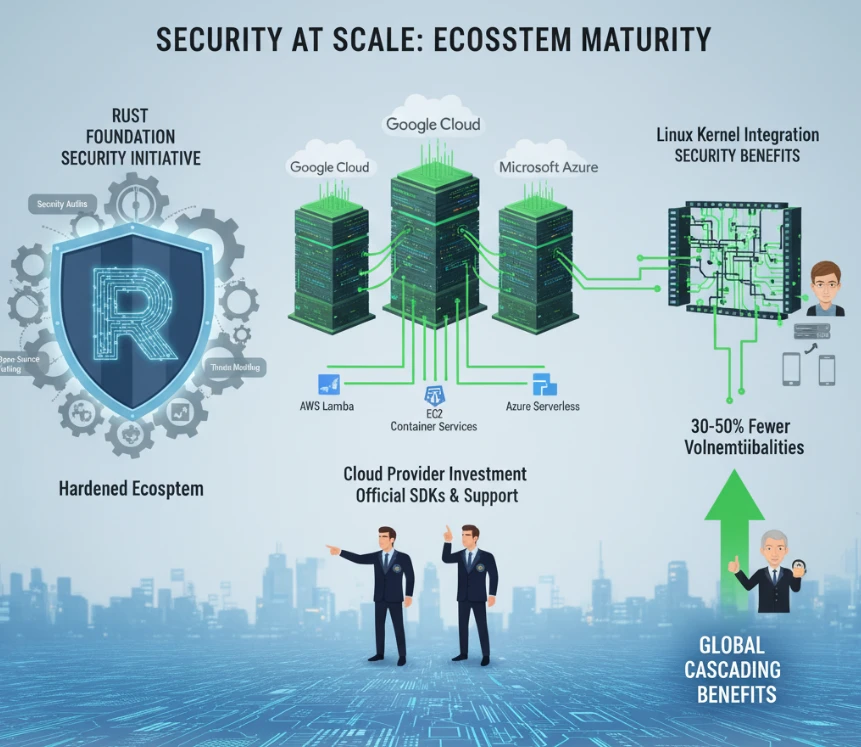
Enterprise adoption depends not just on the language itself but on the surrounding ecosystem. The Rust Foundation’s Security Initiative has systematically hardened the ecosystem through security audits, threat modeling, and development of open-source security tooling. This institutional commitment to ecosystem security distinguishes Rust from earlier languages that treated security as an afterthought.
Cloud Provider Investment
Cloud providers have recognized this maturity by investing in official Rust support. Google Cloud announced an official Rust SDK providing access to more than 140 Google Cloud APIs with built-in authentication, documentation, and code samples designed specifically for Rust developers. AWS continues expanding Rust support across its services, with Lambda functions, EC2 instances, and container services all offering first-class Rust integration. Azure similarly provides Rust support for serverless computing and container orchestration.
These investments signal confidence in Rust’s readiness for enterprise workloads and accelerate adoption across organizations leveraging cloud infrastructure. When major cloud providers invest engineering resources in official SDKs and documentation, it validates the technology’s enterprise readiness and reduces adoption friction for their customers.
Linux Kernel Integration
The Linux kernel itself has become a strategic battleground for memory-safe languages. Linus Torvalds approved Rust integration into the Linux kernel despite initial resistance from some community members, recognizing that kernel-level code represents a critical security perimeter. Security researchers estimate that Rust adoption could reduce kernel vulnerabilities by 30 to 50 percent over five years—a transformation affecting billions of IoT devices, mobile phones, and server infrastructure globally.
This integration represents more than symbolic validation. The Linux kernel powers the majority of internet infrastructure, Android devices, and embedded systems worldwide. Hardening this foundation against memory safety vulnerabilities has cascading security benefits throughout the technology ecosystem.
Addressing Enterprise Concerns: The Hybrid Reality
Prudent enterprise leaders recognize that Rust does not represent a universal solution applicable to every use case. Existing systems, institutional expertise, and specific application requirements mean that most large organizations maintain heterogeneous technology stacks combining Rust, C++, Java, Python, and other languages.
Rather than viewing this as a limitation, sophisticated enterprises leverage Rust strategically. The consensus emerging from enterprise deployment patterns involves identifying the highest-value applications for Rust—typically system software, performance-critical infrastructure, security-sensitive components, and embedded systems—while maintaining pragmatism about legacy systems and broader organizational capabilities.
Strategic Application Areas
The most successful enterprise Rust deployments focus on specific domains where Rust’s advantages shine brightest. Network services that require high throughput and low latency benefit enormously from Rust’s performance characteristics. Security-critical components handling authentication, encryption, or access control gain from compile-time memory safety guarantees. Data processing pipelines that transform petabytes of information daily realize substantial infrastructure savings through Rust’s efficiency.
This pragmatic approach acknowledges that the transition to Rust is evolutionary rather than revolutionary. Organizations need not rewrite entire codebases overnight. Instead, they can adopt Rust incrementally, building expertise while delivering immediate value in targeted applications.
Enterprise-Ready Frameworks
The rise of frameworks specifically designed for enterprise Rust applications facilitates this selective adoption. Mature frameworks like Axum and Actix Web, paired with type-safe database libraries such as SQLx and Diesel, OpenTelemetry integration for observability, and tested patterns for microservices architecture, create a complete enterprise technology stack. Developers can now build sophisticated production systems without accepting performance or reliability compromises.
The ecosystem has matured to the point where enterprises can find production-ready solutions for common requirements: API development, database access, caching, message queuing, logging, monitoring, and deployment automation. This maturity reduces the perceived risk of Rust adoption and accelerates time-to-value for new projects.
Forward-Looking Implications
Several emerging trends suggest that Rust’s role in enterprise software will expand substantially. Artificial intelligence is beginning to influence software development itself—AI-powered tools can now auto-generate device drivers, configuration files, and test scripts from high-level specifications, dramatically accelerating development velocity and reducing boilerplate code. These tools disproportionately benefit memory-safe languages by eliminating an entire category of potential errors in generated code.
Hardware Architecture Evolution
The emergence of RISC-V as a mainstream processor architecture, free from proprietary constraints, creates new opportunities for enterprises to make deliberate choices about their technology stacks. Rust’s ability to run efficiently across diverse hardware platforms, coupled with its ecosystem support for RISC-V and other emerging architectures, positions enterprises to avoid vendor lock-in while maintaining consistent development practices.
This flexibility becomes increasingly valuable as organizations deploy workloads across heterogeneous computing environments: x86 servers in data centers, ARM processors in mobile devices, specialized AI accelerators for machine learning, and emerging RISC-V chips in IoT devices.
Edge Computing and IoT Convergence
Finally, the convergence of edge computing, machine learning, and IoT computing is driving demand for software that handles complex operations within severe resource constraints—precisely where Rust excels. As organizations deploy artificial intelligence to billions of edge devices, the combination of Rust’s safety guarantees and resource efficiency becomes increasingly valuable.
Edge devices often operate with limited memory, constrained processing power, and intermittent connectivity. Rust’s zero-cost abstractions enable sophisticated functionality within these constraints while maintaining the reliability required for autonomous operation in remote or inaccessible locations.
Strategic Recommendations for Enterprise Leaders
For technology leaders evaluating Rust adoption, several strategic considerations emerge. First, focus Rust investments on highest-value applications: infrastructure code, security-critical components, performance-sensitive services, and systems requiring exceptional reliability. These domains generate the maximum ROI while building organizational expertise.
Building Organizational Capability
Second, invest in team development and training. Rust’s learning curve is real but temporary—developers typically report that the ownership model “clicks” within two to three weeks of regular practice, after which productivity increases substantially. Organizations that view Rust training as strategic investment rather than burden position themselves for long-term competitive advantage.
Training should combine formal instruction with hands-on projects that deliver business value. Pairing experienced developers with Rust newcomers accelerates knowledge transfer while maintaining project momentum. Internal documentation capturing organizational patterns and best practices helps codify institutional knowledge.
Ecosystem Selection
Third, prioritize ecosystem maturity over theoretical purity. Select frameworks and libraries with active maintenance, robust documentation, and proven production deployments. The Rust ecosystem has reached sufficient maturity that enterprise-grade applications can be built reliably today, but careful selection of dependencies remains important.
Evaluate libraries based on maintenance activity, community size, security audit history, and compatibility with organizational requirements. Prefer crates with strong type safety, comprehensive error handling, and clear documentation over those offering clever but opaque abstractions.
Pragmatic Integration
Fourth, adopt a pragmatic approach to integration. Rather than attempting wholesale language replacement, identify the highest-impact opportunities and build expertise gradually. Hybrid systems combining Rust with existing technology stacks represent the realistic transition path for most organizations.
Successful integration requires clear interfaces between Rust components and existing systems. Foreign function interfaces (FFI) enable Rust to interoperate with C, C++, and other languages, allowing gradual migration without requiring complete rewrites. Well-defined API boundaries enable teams to work independently while maintaining system coherence.
Conclusion
Rust is reshaping enterprise software not through hype or fashion but through fundamental business value: dramatically improved security, enhanced developer productivity, reduced infrastructure costs, and superior reliability. The convergence of government security recommendations, major cloud provider investment, proven production deployments at scale, and rapidly expanding ecosystem maturity has transformed Rust from an interesting open-source project into a strategic technology that enterprises must seriously consider.
The question for enterprise technology leaders is no longer whether Rust matters, but rather how and where to integrate it strategically into their organizations. The companies that answer this question thoughtfully—investing in the right applications, building genuine expertise, and maintaining pragmatism about integration—will capture substantial competitive advantages in reliability, security, and operational efficiency.
As software becomes increasingly central to competitive differentiation, these advantages compound into strategic superiority that extends far beyond technical considerations into fundamental business outcomes. Organizations that recognize Rust’s strategic value today position themselves for sustained competitive advantage in an increasingly software-defined business landscape.









